Flask Deploy on Apache
This page explains how to deploy a simple Flask application sandboxed with a virtualenv and served by Apache HTTP server using the mod_wsgi module.
Note: this setup was tested on CentOS but can be easily adapted to be executed on other platforms.
Dependencies
- Apache / httpd (on CentOS) server
- mod_wsgi
- Flask web framework
- Python3
- Virtualenv
Prepare the environment
Install Apache server
$ sudo yum install httpd
$
$ # by default the server is down.
$ sudo systemctl start httpd
Install mod_wsgi
$ sudo yum install mod_wsgi
$
$ # restart apache
$ sudo systemctl restart httpd
Test if the mod_wsgi module is loaded
$ sudo httpd -M | grep wsgi
wsgi_module (shared) # <-- the OK response
Install Virtualenv
Virtual environments will sandbox the app to run isolated from the global server environment
$ sudo pip install virtualenv
Code the Flask App
We will use a simple Flask application that serves a simple Hello World message for all routes.
As mentioned before, this setup is executed on CentOs. The steps are:
Go to /var/www - the www_root of Apache server, and create the project directory.
$ cd /var/www
$ mkdir hitme
To have a runnable Flask app, we need to create two files: run.py and app.py inside the app folder. The files are structured as below:
/var/www/hitme
| - run.py
| - app/__init__.py
Where run.py is responsible to bootstrap the Flask app defined in the app directory.
app/init.py file contents
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route("/")
def hello():
return "Hello world!"
run.py file contents
import os
from app import app
#----------------------------------------
# launch
#----------------------------------------
if __name__ == "__main__":
port = int(os.environ.get("PORT", 5000))
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=port, debug=True)
Test the Flask App
We have the test application, now let's start it to see something on the screen. First, we need to create and activate the virtual environment.
$ cd /var/www
$ virtualenv --python=python3 hitme # the venv is created inside the app folder
$ cd /var/www/hitme
$ source bin/activate
At this point, we will run the next commands inside the VENV. Let's install Flask
$ pip install flask
To run, a Flask application require FLASK_APP environment variable.
$ export FLASK_APP=run.py # please notice the name
$ flask run # start the app
$ # our app is running on port 5000
Apache Configuration
To execute a Flask application under the Apache HTTP server we need to bridge our application to the Apache engine using the mod_wsgi module. For this we need to create a new file wsgi.py inside our project folder:
/var/www/hitme
| - wsgi.py
| - run.py
| - app/__init__.py
wsgi.py file contents
#!/usr/bin/env python
import sys
import site
site.addsitedir('/var/www/hitme/lib/python3.6/site-packages')
sys.path.insert(0, '/var/www/hitme')
from app import app as application
The next step is to configure Apache to serve the app and use this wsgi loader. The following settings should be added to the httpd.conf. On CentOS the file location is /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName localhost
WSGIDaemonProcess hitme user=apache group=apache threads=2
WSGIScriptAlias / /var/www/hitme/wsgi.py
<Directory /var/www/hitme>
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
Close and save the file and restart Apache to load the new settings.
$ # restart apache
$ sudo systemctl restart httpd
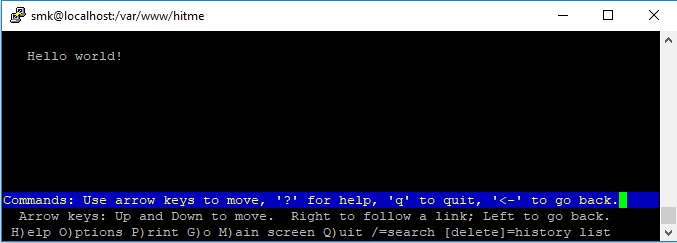
Our Flask app should be served by the Apache HTTP server. We can test the deploy by using lynx command:
$ lynx localhost # lynx